Collections
What is a “collection” in CDS?
A collection is a set of documents that are related to (linked to or from) a single CDS document via a specific set of relationships. The relationships themselves are described later in this document, but the relationship is always a one-to-many relationship from the “parent” document to the “collection” documents.
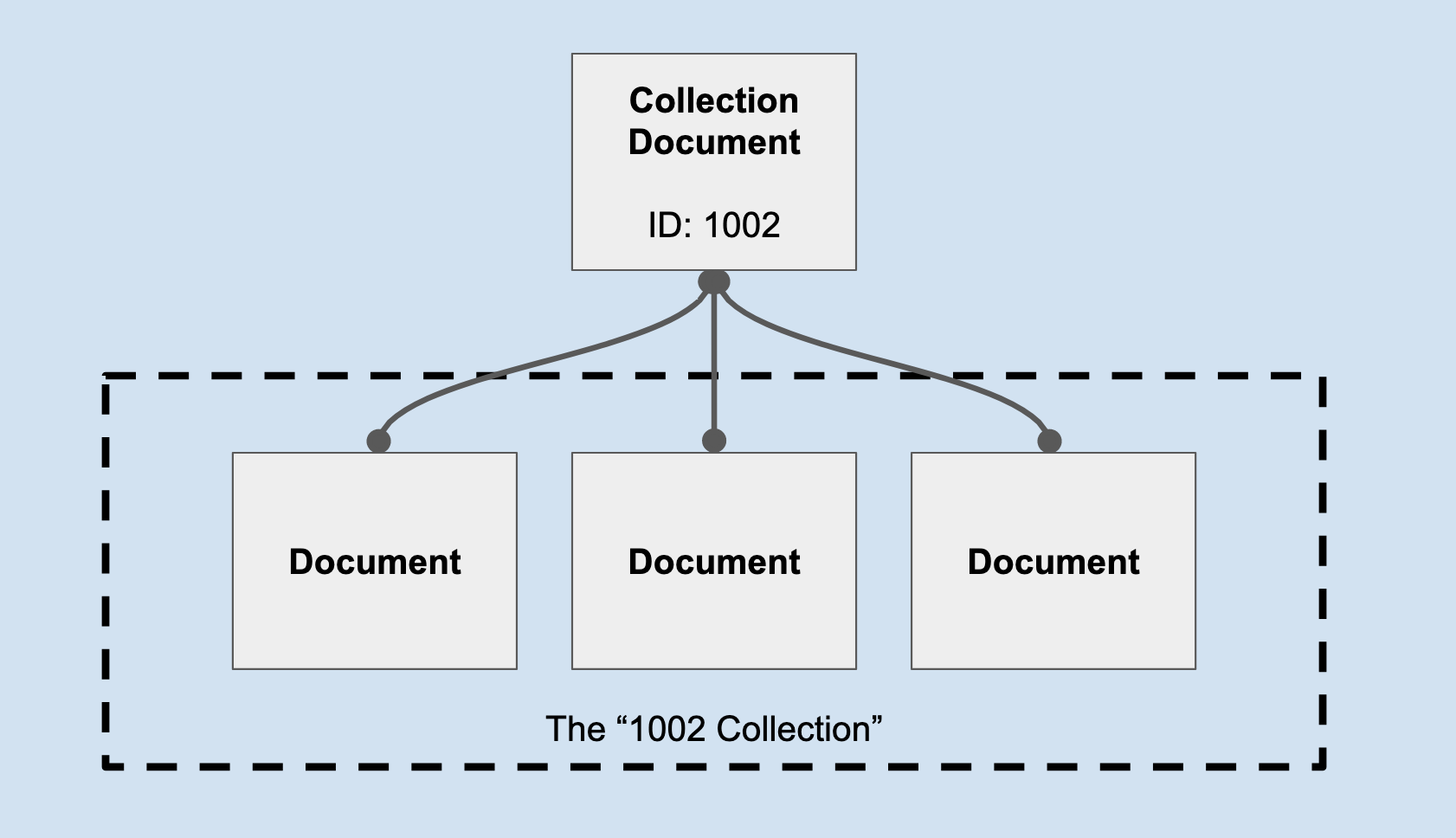
In CDS, any document can be used as a collection. This means topics, tags, series, etc. are collection documents; so are stories, podcast episodes, and categories. For any CDS document, you can ask “what documents are part of this document’s collection?”
Collection links
A document is linked to a collection in one of two ways:
- Unordered - When a document contains a link to its collection document, it’s considered an “unordered” link.
- Ordered - When a collection document contains a link to its “child” document, it’s considered an “ordered” link.
These types of linkages will be described in further detail below.
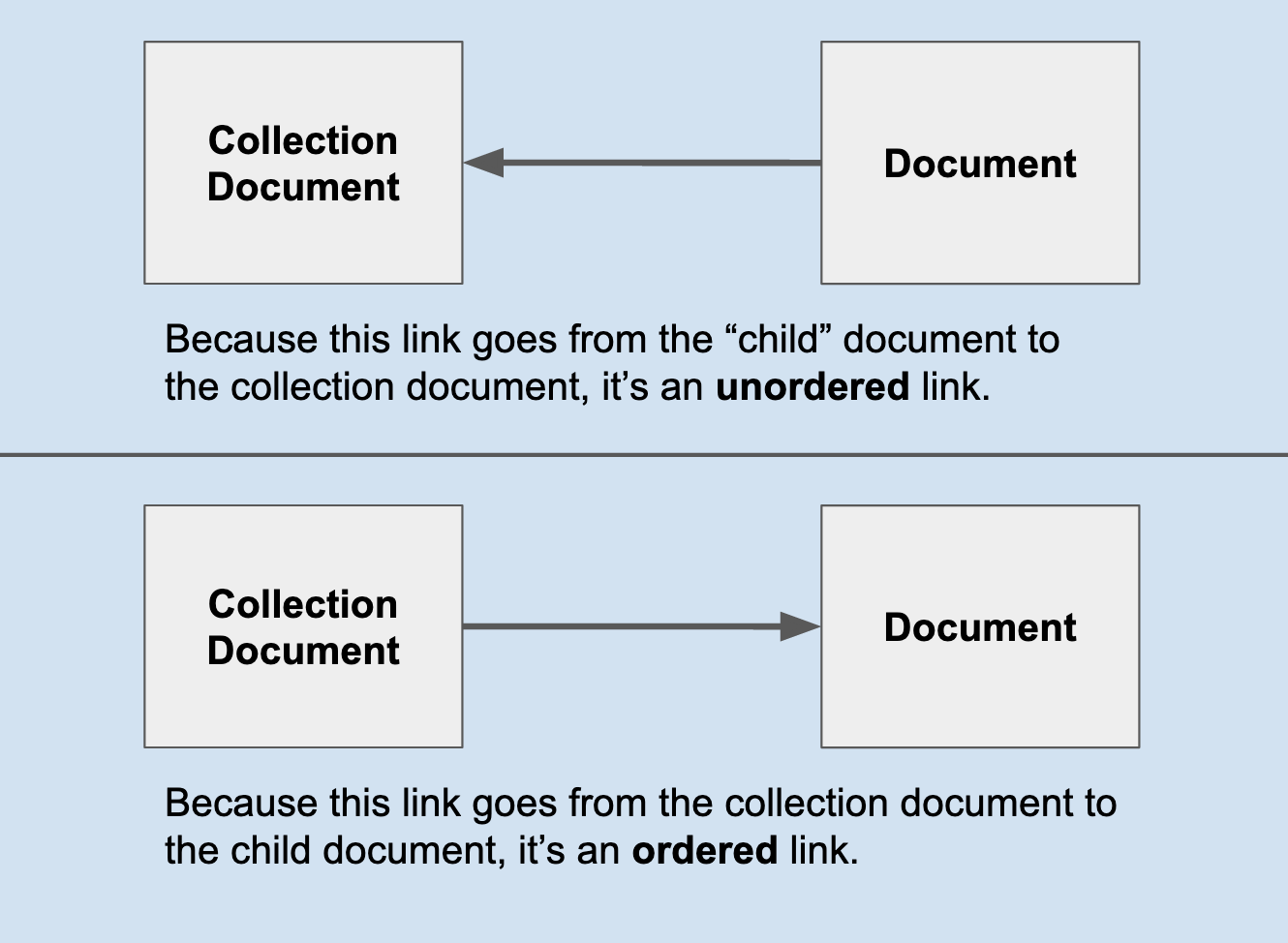
It’s important to remember that a document can be linked to a collection using both ordered and unordered links!
Unordered collection links
As stated above, an unordered collection link exists on the child document and points to the collection document. In practice, this is represented by a link object in the child document’s collections array, defined by the publishable profile:
{
"id": "12345",
"title": "Sleeping patterns of the Norwegian Blue parrot",
...
"collections": [
{
"href": "/v1/documents/6789",
"rels": [
"topic"
]
},
...
]
}
In the above example, document 12345 contains an unordered link to document 6789; 12345 is an unordered document in the 6789 collection.
When retrieving a collection, unordered documents can be sorted in any way the client feels is most appropriate.
Ordered collection links
An ordered collection link exists on the collection document and points to the child document. These links can also be referred to as “prioritized” or “featured” content; this is because these links are usually the result of conscious and deliberate selection (although this is not always the case).
In practice, an ordered link is represented by a link object in the collection document’s items array, defined in the aggregation profile:
{
"id": "6789",
"title": "Animals",
...
"items": [
{
"href": "/v1/documents/12345"
},
...
]
}
In the above example, document 6789 contains an ordered link to document 12345; 12345 is an ordered document in the 6789 collection.
Documents containing ordered links must have the items array; in order to have the items array, they must implement the aggregation profile and list it in their profiles list. These collection documents can also be called “aggregations”. While any document can be a collection document, only documents with the aggregation profile can have ordered collection links.
When retrieving a collection using the editorial sort mode, ordered collection documents will appear first, in the order that they appear in the items array. When using other sort modes, these documents will be sorted along with the unordered documents.
Note that there can be a maximum of 100 links within the items array.
Querying for a collection
When querying for documents, the collectionIds parameter can be used to filter down to documents belonging to a collection:
https://content.api.npr.org/v1/documents?collectionIds=6789
The above query will return only documents that belong to the 6789 collection, regardless of if they are ordered or unordered.
The collectionIds parameter functions like any other CDS query parameter; as such, all the following are valid:
collectionIds=(ID)collectionIds=(ID),(ID)collectionIds=(ID)&collectionIds=(ID)
editorial sort
Editorial sorting is a method of sorting the results of a CDS query that places ordered content before unordered content. When querying for a collection, ordered content will be returned first in the order it appears in the items array, followed by all unordered content sorted by publishDateTime. If a document is linked both as an unordered and ordered document, then its ordered placement takes priority; it will show up once and only once, in the “ordered section”.
Editorial sort can only be used with a single collectionIds parameter defining one collection ID. You cannot combine collections and sort by editorial sort.
Editorial sort is requested with the query parameter sort=editorial.
A note on the idea of a primary collection
This is also explained in the publishable profile documentation.
CDS does not currently offer a way to mark a collection as the primary collection in the rels array. Rather, we rest on a convention that the 0th item in the array for collections is in fact the primary collection.
This is not a convention that is baked in our API, but rather one that npr.org upholds.
The convention also applies more specifically to collections marked with a topic rel or any other type of rel. For example, in this collections array below:
"collections": [
{
"href": "/v1/documents/1182407811",
"rels": [
"series"
]
},
{
"href": "/v1/documents/12345",
"rels": [
"topic"
]
}
]
The primary topic would be the 12345 document, as that is the first collection link listed that has a topic in the rels array.